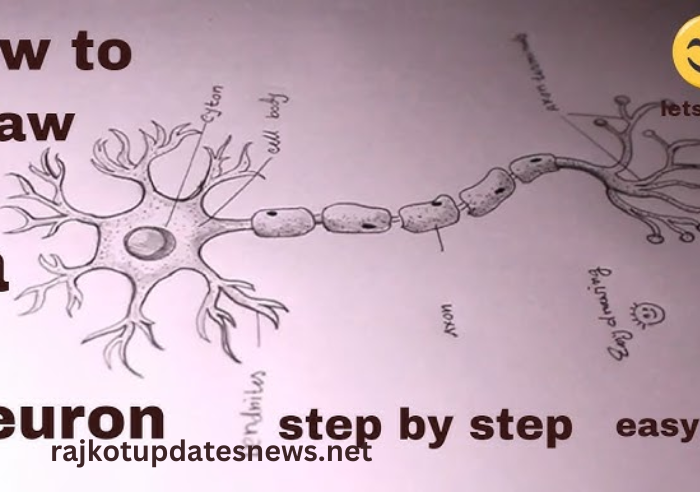
The human brain is a remarkable organ composed of billions of specialized cells known as neurons. These neurons communicate with each other, forming an intricate network that allows us to think, feel, and interact with the world. Understanding how these neurons function is crucial for grasping the overall workings of the brain.
This is where the simple:7gs7_oxii_a= Neuron Diagram becomes an essential tool. It provides a visual representation of the neuron’s structure and its various components, making complex neuroscience more accessible and easier to comprehend.
What Is a Neuron and Its Components?
Neurons are the basic building blocks of the nervous system, responsible for transmitting information throughout the body. Each neuron has three primary components:
- Cell Body (Soma): The cell body contains the nucleus, which houses the cell’s genetic material. It is the metabolic center of the neuron, supporting its overall function and health.
- Dendrites: These are tree-like structures that extend from the cell body and receive signals from other neurons. Dendrites play a crucial role in processing incoming information.
- Axon: The axon is a long, slender projection that transmits electrical impulses away from the cell body to other neurons or muscles. It is often covered in a protective sheath called myelin, which enhances signal transmission speed.
Comparison Table: Components of a Neuron
| Component | Function | Description |
| Cell Body | Contains the nucleus | The metabolic center of the neuron |
| Dendrites | Receive incoming signals | Branched extensions that collect information |
| Axon | Transmits signals to other neurons | Long, thin structure that carries impulses |
How Does the Neuron Diagram Help in Understanding Neuron Functions?
The simple:7gs7_oxii_a= Neuron Diagram serves as a visual guide to understanding how neurons operate. By breaking down the various components, it illustrates the flow of information within the nervous system. For instance, when a neuron receives a signal through its dendrites, that information travels down the axon and is transmitted to other neurons via synapses.
This visual representation helps demystify complex concepts, allowing students and professionals alike to appreciate how neurons work together in networks to perform various functions, such as reflexes and higher cognitive processes.
What Are Synapses and Their Role in Neuron Communication?
Synapses are the junctions where neurons connect and communicate. When an electrical impulse reaches the end of an axon, it triggers the release of neurotransmitters, chemical messengers that travel across the synaptic gap to the receiving neuron. The neuron diagram vividly illustrates these connections, highlighting the role of synapses in neuronal communication.
Understanding synapses is critical because they are the sites where neural information is processed and integrated. For example, in learning and memory, synapses can strengthen over time, a process known as synaptic plasticity.
Note: Remember that synaptic connections can strengthen or weaken based on activity, which plays a vital role in how we learn and adapt.
How Do Different Types of Neurons Function?
Neurons can be categorized into three primary types:
- Sensory Neurons: These neurons transmit signals from sensory receptors (like those in the skin, eyes, and ears) to the brain. They help us perceive our environment.
- Motor Neurons: These carry signals from the brain and spinal cord to muscles, enabling movement and coordination.
- Interneurons: Found primarily in the brain and spinal cord, interneurons connect sensory and motor neurons, facilitating communication within the nervous system.
The simple:7gs7_oxii_a= Neuron Diagram often incorporates these distinctions, illustrating how each type plays a unique role in the nervous system. Understanding these differences is crucial for comprehending how sensory information is processed and how responses are generated.
What Is Neuroplasticity, and How Does It Relate to Neuron Diagrams?
Neuroplasticity is the brain’s ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections throughout life. This remarkable capacity allows the brain to adapt to new experiences, learn new information, and recover from injuries. The neuron diagram helps visualize these changes, showing how experiences can reshape neuronal pathways.
For instance, when a person learns a new skill, such as playing a musical instrument, the connections among neurons in relevant areas of the brain can strengthen and multiply. This process illustrates the dynamic nature of the brain, as it constantly adapts based on experiences.
Reminder: Keep in mind that neuroplasticity varies by age and individual experiences, emphasizing the brain’s adaptability and its capacity to learn throughout life.
Why Is Understanding Neurons Important for Mental Health?
A solid understanding of how neurons function can provide valuable insights into various mental health conditions, such as depression, anxiety, and schizophrenia. Imbalances in neurotransmitters can significantly impact mood and behavior, making it essential to comprehend how these chemical messengers operate within the neuron network.
The simple:7gs7_oxii_a= Neuron Diagram serves as a foundational tool for exploring these concepts. For example, knowing how serotonin and dopamine influence emotions can aid in understanding treatment approaches for mood disorders.
How Do Neurons Contribute to Overall Brain Function?
Neurons do not operate in isolation; they work together to create neural circuits that perform complex tasks, such as memory, decision-making, and emotional regulation. The neuron diagram acts as a roadmap for understanding these interconnected systems, illustrating how dysfunction in one area can lead to broader cognitive issues.
For instance, a disruption in the communication between neurons involved in emotional regulation can contribute to mood disorders, highlighting the importance of maintaining healthy neural networks for overall mental well-being.
Conclusion
The simple:7gs7_oxii_a= Neuron Diagram is an invaluable tool for visualizing and understanding the complex world of neurons. By breaking down the anatomy and functions of neurons, this diagram illuminates the intricacies of brain health and cognition.
Whether you’re a student, a healthcare professional, or simply curious about the brain, familiarizing yourself with this diagram can deepen your appreciation for the wonders of neuroscience.
FAQ’s
- What is the simple:7gs7_oxii_a= Neuron Diagram used for?
It is used to visualize and understand the structure and function of neurons. - How do neurons communicate with each other?
Neurons communicate through synapses using neurotransmitters to transmit signals. - What are the main components of a neuron?
The main components are the cell body, dendrites, and axon. - Why is neuroplasticity important in learning?
Neuroplasticity allows the brain to adapt and form new connections, which is crucial for learning new skills. - How can understanding neurons benefit mental health?
It helps in recognizing how neurotransmitter imbalances affect mood and behavior, informing treatment approaches.